Building assessment items requires significant investment of effort and resources. It is always desirable from a teacher’s perspective to be able to reuse technically sound test items. Shilpi Banerjee and Bijay Das discuss the concept of an item bank and introduce a simple approach that can help teachers create and maintain item banks effectively.
An item bank is a purposefully created robust repository of assessment items in which items are organised and categorised based on their characteristics such as subject, grade, cognitive level, content domain, and item type.
Why is an item bank useful?
Ensures the quality of assessment items
An assessment item is designed for assessing the attainment of a specific learning outcome for a subject and grade. Learning outcomes are expressed in terms of cognitive skills that students should demonstrate and content they should acquire. A valid assessment item should be aligned well with learning outcomes. To ensure this alignment, important information related to an assessment item such as content domain, cognitive level, subject, grade, and difficulty level is stored in the form of metadata. Item banks have the provision to store this metadata which helps to identify the right set of items while designing an assessment instrument. Also, the accuracy of assessment items is established through multiple levels of pedagogical and technical review before they are pooled in the item bank.
Provides ease of developing assessment instruments
Assessment instruments are used for multiple purposes ─ to test how well a student can demonstrate the acquired knowledge, skills, and dispositions in a subject, to identify misconceptions and learning gaps, for grading or certification, and to ensure accountability in education systems. It is important that teachers follow certain principles to ensure that assessment instruments:
- are well aligned to the curricular goals
- assess a range of cognitive dimensions of learning
- are not predictable
- evaluate in a fair, transparent, and credible manner
Item banking is one of the critical steps in the development of a high-quality assessment instrument. A well-organised item bank helps in supplying items and their scoring guides as per the desired blueprint (elaborated below) during the development of an assessment instrument.
However, an item bank needs to be managed appropriately; if it is not managed well, reusing existing items may pose significant challenges.
Architecture of an item bank
An item bank is usually designed using professional item banking software. We are proposing the use of Moodle software which is already widely used by educators for online classes and can be used for item banking.
Moodle is an open-source learning management system designed to help teachers create online courses: sharing learning resources, handling assessment submission, monitoring student progress, and managing grade books.
It also has a feature for creating an online item bank where items can be created, reviewed, and used for designing an assessment instrument. Moodle versions 3.9 and 3.10 may be preferred over older versions for developing an item bank.
They provide an additional feature that allows item search based on metadata along with other routine features such as the creation of users and items, and review of items and pool items for assessment instrument development.
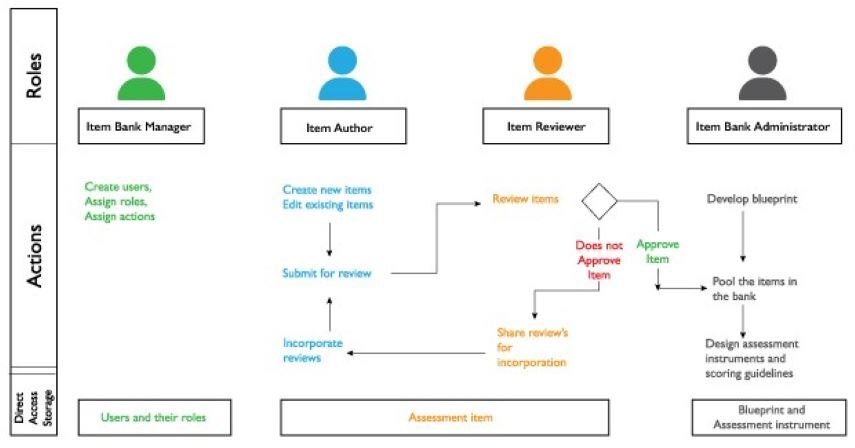
The item bank framework outlines the different roles of members, their actions, and what can be stored and used for effective teaching and learning.
- The item bank manager adds new users and assigns them different roles such as item author, item reviewer, and item bank administrator. Each of these roles undertake specific actions in the development of an item bank.
- The item author creates new items and tags them with necessary metadata. These items are submitted for review to item reviewers along with their scoring guides.
- The item reviewer examines the items to check their alignment with a learning outcome, factual accuracy, quality of the stimulus material used, robustness of the scoring guide, and sensitivity issues in items. These items are approved only if they meet the quality parameters; otherwise, they are sent back to the item author with the relevant review comments. Approved items are pooled in the item bank and can be used while designing an assessment instrument.
- The item bank administrator creates a blueprint for the structure of the assessment instrument. The blueprint represents the distribution of marks across different content domains, cognitive levels, and item types. The items that align well with the parameters stated in the blueprint are selected automatically to develop an assessment instrument.
The item bank provides an efficient way of storing and reusing assessment items. Once an item has been developed and tagged uniformly, a teacher can search through the tags and identify the relevant assessment items in alignment with the lesson plan for that day.
These identified assessment items form the basis of facilitation of learning outcomes during classroom teaching and assessment. To use the existing assessment items for summative assessment, a teacher needs to carefully design a blueprint, search relevant assessment items as per the blueprint using tags, and assemble them to develop an assessment instrument.
Therefore, it is worthwhile for school teachers to invest time in building such an item bank to enable efficiency and effectiveness in the development of a quality assessment instrument for both formative and summative purposes.
Have you used an item bank at your school? Were you a part of the item bank development process? What are some of the challenges in developing robust assessment items?



